 Click to visit the previous Marine Specie bio
Click to visit the previous Marine Specie bio
 |
|
 |
|
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Reptilia
SuperOrder: Sauropterygia
Order: Nothosauroidea
Family: Nothosauridae
Genus: Nothosaurus
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|

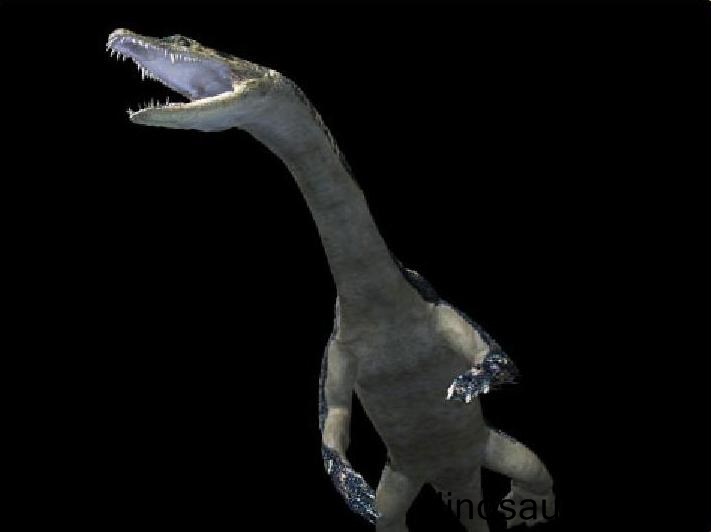
The Nothosaurus was a marine reptile which existed on the earth during the middle to late Triassic period. It belonged to family Nothosauridae, which consisted of moderately sized, semi aquatic Mesozoic vertebrates. It was not a dinosaur, as may be suggested by its name.
The Nothosaurus was in existence about 245 to 209 million years ago. This phase lies between the Anisian and Norian ages of the Triassic period. Nothosaurs were adapted to living on land as well as water and the Nothosaurus was no different. Its lifestyle resembled that of modern day sea lions and seals. It hunted exclusively in water but intermittently came ashore to bask in the sun.
The size of the Nothosaurus was modest as compared to other marine vertebrates such as the ichthyosaurs and the plesiosaurs. Its length is estimated to be about 9 to 11 feet. Its mass is believed to have been 80 to 150 kilos.
The Nothosaurus is the best defined genus of order Nothosauroidea. Its fossils have been discovered in abundance in Europe and Asia. More than ten sub species of the Nothosaurus are known today. This shows that it was present in large numbers and was ubiquitous on the eastern shores of Pangaea, the Triassic supercontinent.
Etymology
The prefix ‘nothos’ translates to ‘fake’. The suffix ‘-sarus’ is derived from the Greek word ‘sauros’. It means ‘lizard’ in English. Thus, the name Nothosaurus roughly translates to ‘a fake lizard’.
When the fossils of the Nothosaurus were first discovered the early 1800s, marine reptiles were not described in detail. Even clade Dinosauria was not defined. Its fossils made it look like a land dwelling organism but since it was not quite as it looked, the name ‘Nothosaurus’ was selected for it.
The type species Nothosaurus mirabilis means ‘remarkable’ in Latin. Aquatic reptiles were a new find during the beginning of the nineteenth century.
The nomenclature of these fossils was done by G. Munster.
Discovery of fossils
- The holotype of the Nothosaurus was discovered in Germany in the rock formation Muschelkalk. It was found in the year 1833.
- Subsequently, many fossils were discovered in other German towns such as Osnabruck and Hohenlohe.
- Bones have also recovered from Holland, Spain, France and Switzerland.
- There were certain skeletons which were excavated in the Guizhou district of China and the Maktesh Ramon in Israel, and were attributed to the Nothosaurus.
- Fossils ascribed to the Nothosaurus have been discovered from the African continent as well.
Most of the fossils discovered comprised of complete, well-articulated skeletons. As such a vast amount of information is available about the Nothosaurus, many of its sub species are very clearly defined.
Current location of fossils
The Naturkunde Museum in Berlin currents hosts a complete skeleton of the Nothosaurus.
Classification
- The Nothosaurus is classified under super order Sauropterygia, family Nothosauridae and sub family Nothosaurinae.
- The genus Nothosaurus was described in 1834, but the sub family Nothosaurinae was coined almost a century later in the year 1923. The family Nothosauridae was defined another forty years later in 1965.
- Thus it can be seen that the classification of the Nothosaurus was a gradual process. At the time of its discovery, scientists were clueless about its lineage and relatives.
- Many fossils of the Nothosaurus have been incorrectly grouped under separate genera. Most of these genera have been unrecognized today, such as Chondrisaurus, Dracosaurus, Elmosaurus, Shingyisaurus, etc.
- The German subspecies include the N. mirabilis, N. edingerae; the Chinese subspecies are the N. rostellatus, N. youngi and N. yangjuanensis; the Israeli subspecies include the N. tchernovi and the N. haasi. Many more sub species are currently defined.
The Muschelkalk
The Muschelkalk is a natural geological formation situated in Europe. Most of it contained in Germany. The Muchelkalk, along with the Keuper and Buntsandstein forms the German trio of rock formations. The Triassic period derived its name from this triad.
The German Muschelkalk is divided into three segments, the Upper, Middle and Lower. The Upper segment consists of uniform layers of limestone, the Middle segment comprises of dolostone and gypsum and the Lower subdivision has wavy layers of ooids and limestone.
The fossils found in this formation are almost exclusively form the Triassic period of the Mesozoic era.
Georg Munster
Georg zu Munster was a German count and a geologist. He was an avid fossil collector is credited with discovering many bones from the German rock formations.
Munster was born in Langelage in Germany to a wealthy family. He undertook an administrative position in the year 1800 in the province of Bayreuth.
He passed away in Bayreuth at the age of sixty eight and the Graf-Munster Gymnasium in Bayreuth was named in his honor posthumously.
Physical features
- The Nothosaurus achieved an adult length of around 3.5 to 4 meters. Its weight is speculated to be about 150 to 300 pounds.
- It possessed a small head and a long jaw which had sharp teeth. These teeth were numerous and interlocking.
- The neck of the Nothosaurus was long, yet its flexibility is questionable.
- The Nothosaurus had webbed hands and feet. This modification shows that it not completely adapted for an aquatic lifestyle.
- The tail of the Nothosaurus was long and stout and it aided changing directions while swimming.
Habits and habitat
The Nothosaurus was most certainly carnivorous. Its diet was believed to consist only of fish at some point. But after placodont fossils were found inside the skeleton of the Lariosaurus, a basal nothosaur, scientists believed its diet to be more varied.
Due to its webbed legs, the Nothosaurus is presumed to be poor swimmer. It most likely relied on the element of surprise to capture its prey. After feeding in water, the Nothosaurus most probably retreated back to land much like modern pinnipeds. While on land, it had to be wary of theropod dinosaurs.
The habitat of the Nothosaurus consisted of sea shores and shallow waters. Its presence was seen all across the Atlantic Ocean.
Related species
The Nothosaurus was closely related to nothosaurs such as the Ceriosaurus and the Lariosaurus and distantly related to the Keichosaurus. Plesiosaurids are believed to have evolved from nothosaurs and thus the Nothosaurus is distantly related to the Plesiosaurus.
Final notes of the Nothosaurus
The Nothosaurus is the archetypal nothosaur. It was present in larger numbers during the prime of its existence.
It was an intermediate species between terrestrial and aquatic organisms and hence scientists are keen to study it even today.
Index
Extinct Profiles
 Triassic Dinosaurs
Triassic Dinosaurs Jurassic Dinosaurs
Jurassic Dinosaurs Cretaceous Dinosaurs
Cretaceous Dinosaurs Pterosaurs
Pterosaurs Marine Reptiles
Marine Reptiles Dinosaur Extinction
Dinosaur Extinction