 Click to visit the previous dinosaur bio
Click to visit the previous dinosaur bio
 |
|
 |
|
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Sauropsida
SuperOrder: Dinosauria
Order: Theropoda
Family: Dilophosauridae
Genus: Dilophosaurus
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
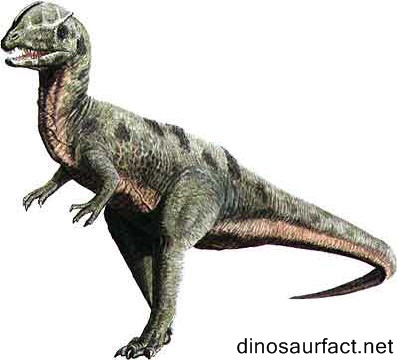
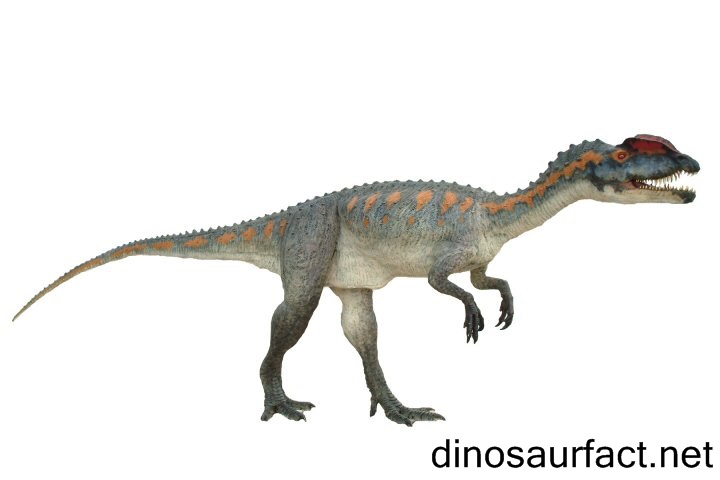
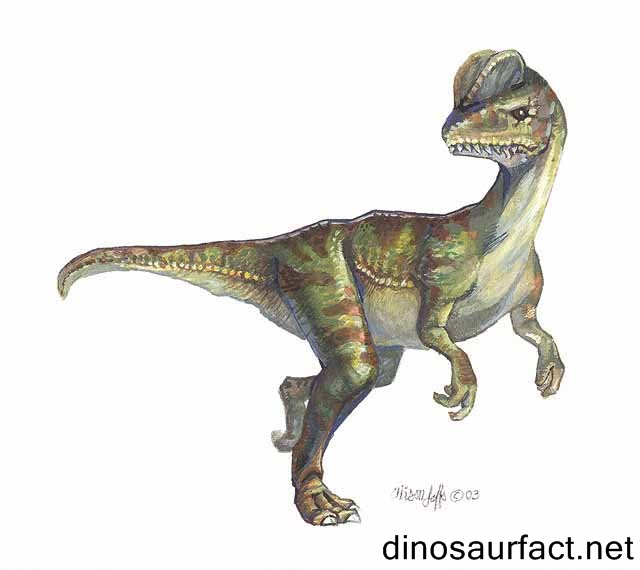
The Dilophosaurus was an early Jurassic dinosaur. It existed on the earth about 199 to 189 million years ago. This period extended from the Hettangian to the Pliensbachian ages of the Jurassic. It was a carnivorous, bipedal dinosaur.
The Dilophosaurus is classified under sub order Theropoda. Its fossils were discovered in North America. Like other Lower Jurassic theropods, it was moderately large in size, growing to an average adult size of about 6 to 7.5 meters. Its weight is estimated to be around 500 to 600 kilos. Such dimensions were modest as compared to the larger Cretaceous theropods which could weigh ten times as much.
The most prominent features of the Dilophosaurus were the ridges present on its skull. These formed a large part of its head and were believed to be embellishments only. They were very fragile to be used as a weapon.
The movie Jurassic Park has shown the Dilophosaurus having a distinctive retractable hood. There is no evidence that the Dilophosaurus possessed such a structure. If it did, it would be composed of soft tissue; and soft tissues are difficult to judge based on bony remains.
Nomenclature
The Dilophosaurus is named after its conspicuous crests. The prefix 'di' stands for 'two'. The word 'lophos' is a Greek word denoting 'ridge'. The suffix '-saurus' is derived from the Greek word 'sauros' which translates to 'lizard'. Thus the name 'Dilophosaurus' means 'a lizard with two ridges'.
The binomial name Dilophosaurus wetherilli was derived from the species name of the Megalosaurus.
The fossils were named by paleontologist Samuel Welles.
Discovery of fossils
- The fossils of the Dilophosaurus were discovered in the Kayunga Formation in Arizona in the year 1942. They were uncovered by Samuel Paul Welles. He examined them and found them to belong to the Megalosaurus.
- When he revisited Arizona a few years later, he found another set of remains similar to the first ones except these had very distinctive ridges. He named these remains Dilophosaurus in 1970 and reclassified the first set under this genus.
- A few more fossils were discovered in Arizona which were considered to be sub species of the D. wetherilli by Samuel Welles.
- More recently, some remains were discovered in the Dharmaram Formation in southern India which are currently attributed to the Dilophosaurus.
Classification
- The Dilophosaurus is currently classified under sub order Theropoda and family Dilophosauridae.
- Over the years, the remains of the Dilophosaurus have been shifted around in sub order Theropoda several times.
- The holotype was classified under family Megalosauridae by S. Welles.
- In the 1980s, it was classified under family Coelophysidae.
- In the early 2000s scientists were speculating that the dinosaur was related to clade Tetanurae.
- Samuel Welles believed that the Dilophosaurus had two sub types, one with the crests and the others devoid of it. He named the non-ridged variants Dilophosaurus breedorum. But he passed away before he could publish his hypothesis. Currently only one species, the D. wetherilli is officially recognized.
- A few bones were found in China in 1987 which were believed to belong to the Dilophosaurus. These were later found to belong to the Sinosaurus.
Current location of fossils
The Kayenta Formation
The Kayenta Formation is a natural structure composed of sedimentary rocks. It involves the central states of America, primarily Utah, Arizona and Colorado. It is composed of sandstone and siltstone.
The overall color of the formation is red to brown. As many rivers were present here during the Jurassic period, the siltstone layers are ubiquitously seen here.
The depth of the formation is about 120 meters. Dinosaur footprints are found very commonly here. Fossils of dinosaurs such as the Sarahsaurus, Megapnosaurus and Scutellosaurus were discovered here along with those of the Dilophosaurus.
Physical features
- The Dilophosaurus was a comparatively small sized theropod. Its size at full growth was about 20 to 23 meters. Its final weight is estimated to be 0.5 to 1.2 metric tons.
- The obtuse ridges or crests along its nasal and lacrimal bones were the most noticeable adaptations of the Dilophosaurus. It was the first theropod to show such structures.
- The skull of the Dilophosaurus was large as compared to its body.
- The Dilophosaurus had reduced forelimbs. This was a common feature amongst theropods. They were not as short and stiff as those of the Tyrannosaurus.
- The femur of the Dilophosaurus was longer than its tibia. This shows that could not sprint fast.
- The Dilophosaurus had a long tail. It was used for maintaining balance.
- There is no data showing physical differences between male and female dinosaurs in the fossils of the Dilophosaurus.
- The dissimilarities of the crest amongst the various Dilophosaurus specimens have not been investigated thoroughly. Some paleontologists believe that the specimens with the smaller crests were juvenile.
Habits and habitat
- The Dilophosaurus was a biped, i.e. it could walk on two feet. It most likely did not walk erect; its center of gravity was located a little cranially from the thighs.
- It had carnivorous feeding habits. It hunted other dinosaurs and vertebrates. But a scavenging habit cannot be dismissed for the Dilophosaurus.
- Some scientists believe that the Dilophosaurus lived or hunted in packs. This was because the fossilized remains invariably had a group of individual together. But others postulate that floods and other such calamities would have brought many bodies and remains at a single location. There is no other indication supporting this theory.
- The habitat of the Dilophosaurus consisted of abundant rivers, streams and other water sources. Rainfall was most likely heavy in its environment.
Related and coexisting species
According to most recent opinions, the Crylophosaurus is considered a close relative of the Dilophosaurus. The Zupaysaurus, Liliensternus and the Coelophysis may also have been related to the Dilophosaurus.
The Dilophosaurus may have coexisted with the Scutellosaurus, Anchisaurus, Ammosaurus, Megapnosaurus etc. Many other aquatic invertebrates, along with fishes and crocodilians may also have shared their habitat with the Dilophosaurus.
Epilogue
The appearance of the Dilophosaurus was unique. The presence of elevations and rims on the skull of theropods was first seen when the Dilophosaurus was discovered. The utility of these structures was difficult to determine for lack of evidence to compare them with.
The study of the Dilophosaurus has immensely helped scientist understand other horned theropods.
Just for fun we have a soundclip available for you to hear what a Dilophosaurus could've sounded like. Click to the Dinosaur Sounds area to hear it. Please note that the dinosaur sounds are only for entertainment and are not an actual fact
Index
Extinct Profiles
 Triassic Dinosaurs
Triassic Dinosaurs Jurassic Dinosaurs
Jurassic Dinosaurs Cretaceous Dinosaurs
Cretaceous Dinosaurs Pterosaurs
Pterosaurs Marine Reptiles
Marine Reptiles Dinosaur Extinction
Dinosaur Extinction