 Click to visit the previous dinosaur bio
Click to visit the previous dinosaur bio
 |
|
 |
|
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Sauropsida
Superorder: -Not Described-
Order: -Not Described-
Genus: Spondylosoma
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
The Spondylosoma was a Triassic vertebrate that was likely existent in the Ladinian age. It roamed the earth about 240 to 235 million years ago. The exact taxonomic location of the Spondylosoma is arguable. Some scientists believe it belong to clade Dinosauria, with it being a primitive saurischian. Others postulate that it should be classified under clade Archosauria.
In spite of this disparity of opinion, the detection of the Spondylosoma has been monumental for studying the origin of dinosaurs and other related species.
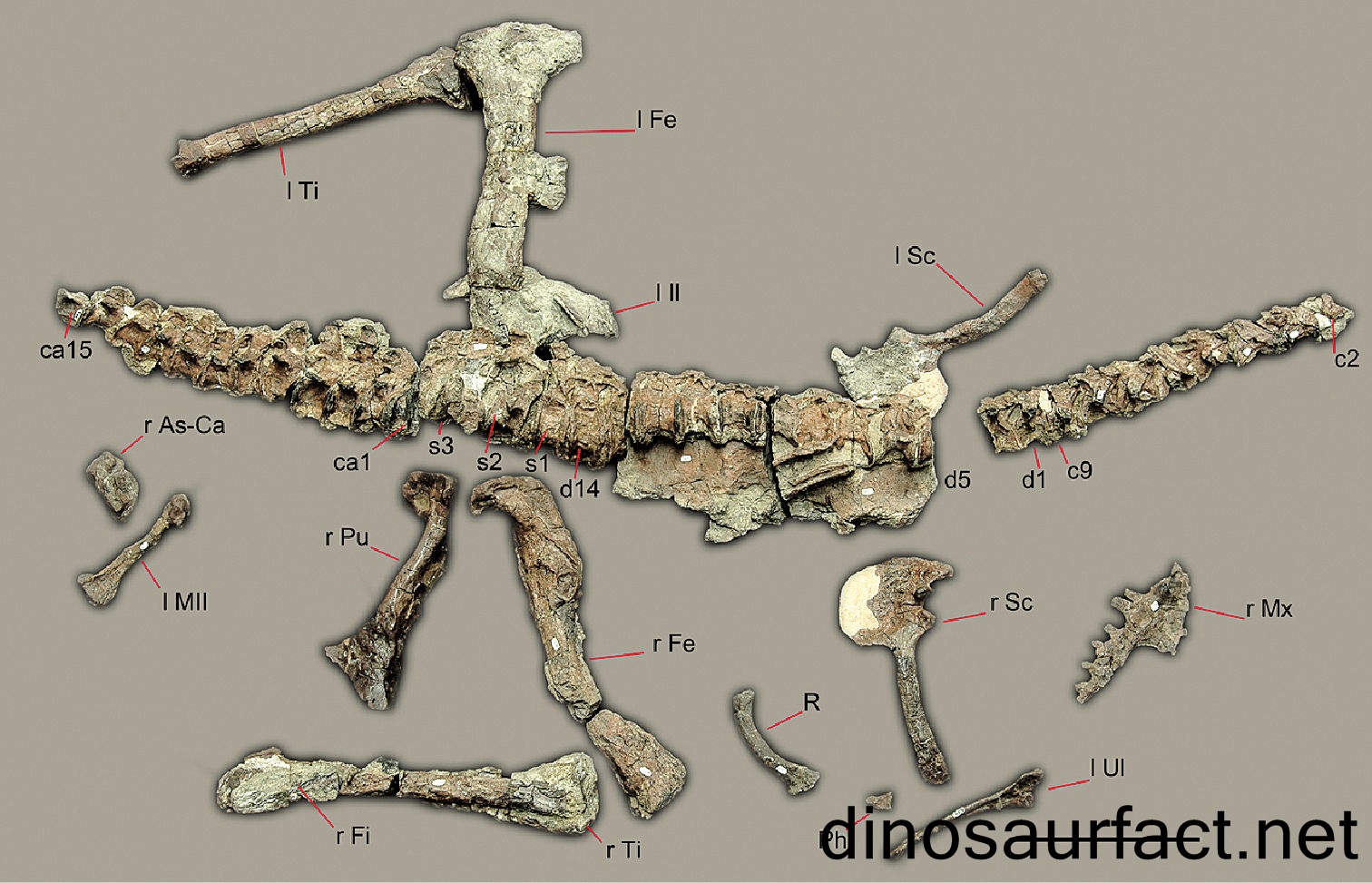
Based on the skeletal remains, it can be determined that the Spondylosoma was a small dinosaur reaching an adult size of about 6.5 to 7 feet from head to tail. Its tail constituted much of this length. The weight of the Spondylosoma possibly was a modest 20 to 30 kilos.
It is one of the earliest vertebrates discovered that at least partly resembles dinosaurs.
Nomenclature
The term ‘spondylo’ is used to indicate ‘vertebrae’ or the ‘spine’. The suffix ‘-soma’ is derived from the Sanskrit word ‘sauma’ or ‘som’ which denotes the ‘body’, as a distinction from the soul. Thus the word ‘spondylosoma’ translates to a ‘body made out of vertebrae’.
This name was probably chosen to signify that the Spondylosoma was a vertebrate creature. Not much else is known about the organism.
The name was suggested by Friedrich von Huene, a German paleontologist.
The specific name Spondylosoma absconditum was used to indicate the lack of information available about the Spondylosoma.
Classification
- The remains ascribed today to the Spondylosoma were originally examined by Friedrich von Huene in 1942. He presumed them to belong to a basal sauropodomorph after examination. Thus he classified the Spondylosoma as a dinosaur.
- Since then there have been as many opinions as scientists about the lineage of the Spondylosoma. It has been called a rauisuchian, a prosauropod and even an archosaur.
- Recently, Peter Galton has found the Spondylosoma to be more closely related to group Rauisuchia, thus stating it did not belong to clade Dinosauria.
- But Max C. Langer, in 2004, has classified the Spondylosoma as a theropod dinosaur related to family Herrerasauridae. But he has also acknowledged the resemblance to rauischian species.
Only when more Triassic fossils will be discovered shall the classification of the Spondylosoma be clearer.
Discovery of fossils
The remains of the Spondylosoma were discovered in the Lower Santa Maria Formation of Brazil. They were excavated in the geopark of Paleorrota. The Paleorotta has been the source of many dinosaur fossils of the Triassic period.
Nature and types of fossils
Many of the bones of the Spondylosaurus were discovered in Brazil.
- Two teeth were found which helped understand the jaw bones of the Spondylosaurus.
- A few cervical and thoracic vertebrae were also uncovered.
- The scapula and humerus offered good information about the forelegs of the Spondylosaurus.
- The sacrum, a partial pubis and the femur were also discovered, which shed light on it hind legs and gait.
The elongated cervical vertebrae are characters of prosauropod dinosaurs. But the features of the sacral vertebrae are more like non-dinosaur species.
Thus, based on the characteristics of the fossils, the Spondylosoma is a very interesting intermediate species.
Current location of fossils
The University of Tubingen currently hosts the remains of the Spondylosoma. Tubingen was incidentally the native town of F. von Huene.
The Santa Maria Formation
The Santa Maria Formation is a natural structure composed of sedimentary rocks in Brazil. It is a part of the Paleorrota, which is comprised of the following groups
- The Serra Geral Formation
- The Botucatu Formation
- The Guara Formation
- The Santa Maria Formation
- The Sanga do Cabral Formation
- The Piramboia Formation
- The Itarare group
Dinosaurs such as the Saturnali, Teyuwasu and the Staurikosaurus were discovered in the Santa Maria Formation, along with the Spondylosoma.
Friedrich von Huene, Peter Galton and Max Langer
- Freidrich von Huene was a German scientist who was single handedly responsible for developing the modern method of taxonomic classification. He has probably analyzed and classified more dinosaur species than any other paleontologist of the twentieth century.
- Peter Galton is a contemporary British paleontologist who is currently working in the United States. He has worked extensively with the remains of the Plateosaurus.
- Max Cardoso Langer is young Brazilian paleontologist who has had remarkable success amongst the Brazilian dinosaur species. He is currently associated with the University of Sao Paulo.
Physical characteristics
The Spondylosoma was petite in size, which was a feature commonly seen amongst mid Triassic vertebrates. It attained an adult size of about 2 to 2.5 meters. It perhaps weighed no more than 50 to 60 pounds.
As both forelimb and hind limb bones have been found, it is known that Spondylosoma was a bipedal organism. It was a fast sprinter, as indicated by its extremities.
It had a tiny skull and a whip like tail.
Habits and habitat
- As only a few teeth fossils are available that are attributed to the Spondyloma, it is difficult to determine whether it was a carnivore or a herbivore.
More scientists believe that it was carnivorous as rauischians and basal saurischians were meat eating. Furthermore, the Staurikosaurus, which was also discovered in Brazil, was a carnivore. Many paleontologists believe Spondylosoma to be related to the Staurikosaurus.
On the other hand, basal sauropods were herbivorous.
An omnivorous feeding habit cannot be overlooked for the Spondylosoma.
- The habitat of the Spondylosoma consisted of woodlands well supplied with rivers and lakes. These water sources probably disappeared during summer when the climate was very hot.
Related and coexisting species
The fossils of the Spondylosoma show similarities to many vertebrate groups such as dinosaurs, archosaurs and rauischians. It is believed that the Spondyloma could be related to the Staurikosaurus.
The Spondylosoma could possibly have coexisted with organisms such as the Lagerpeton and the Lagosuchus.
Epilogue
The information existing about the Spondylosoma is vague and confounding. It resembles a host of creatures from Ladinian and Carnian ages of the Triassic period. Its fossils clearly display the diversification of species seen in the middle Triassic.
Although the precise classification of the Spondyloma is not agreed upon, paleontologists were very excited about its discovery. It indicated that there may be many more vertebrate fossils in the world yet undiscovered.
The Spondyloma fills up many of the gaps in the modern understanding of the Triassic fauna.
Index
Extinct Profiles
 Triassic Dinosaurs
Triassic Dinosaurs Jurassic Dinosaurs
Jurassic Dinosaurs Cretaceous Dinosaurs
Cretaceous Dinosaurs Pterosaurs
Pterosaurs Marine Reptiles
Marine Reptiles Dinosaur Extinction
Dinosaur Extinction